To see the recap on 2019 software testing trends, read our article here.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Testing
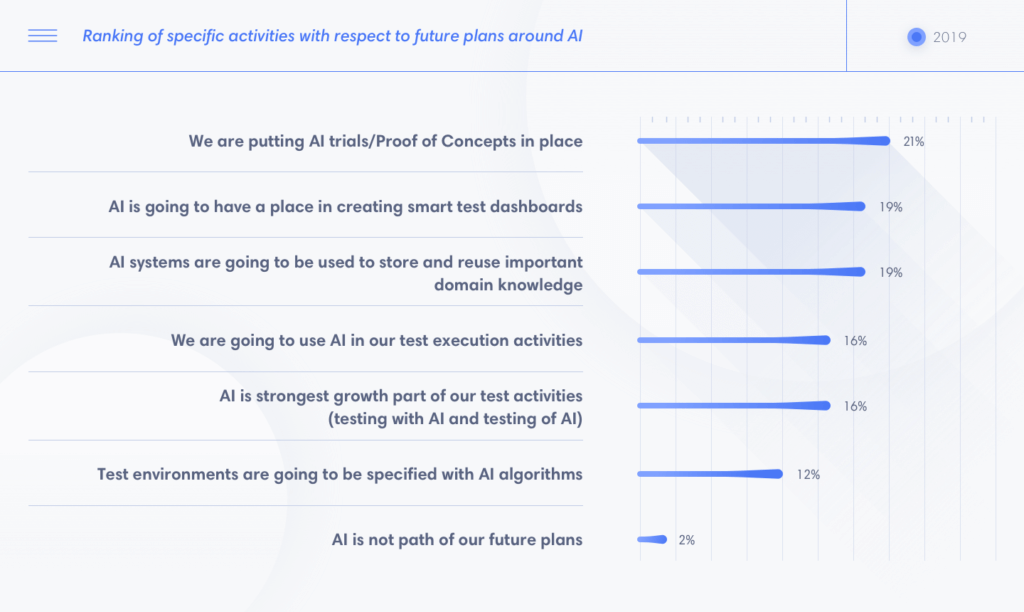
Intelligent automation will continue to be on the software testing radar in 2020, according to a variety of reports.Applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) have been leveraged in software test automation before. AI makes testing smarter. Teams can leverage AI/ML to optimize their automation strategies, adapt faster, and operate more effectively.
In 2019, quality assurance (QA) teams have applied AI/ML in predicting test quality, prioritizing test cases, classifying defects, detecting test objects, interacting with applications under tests (AUT), and so on. It is expected that AI will be omnipresent in every sphere of innovative technology. Investments in this area are expected to fall around $6-to-7 billion in North America alone. By 2025, it is forecast to reach nearly $200 billion. We will expect to see applications of AI in more testing areas — most of which will be relevant to reports and analytics:
- Log analytics: Identify unique test cases that need manual and automated testing
- Test suite optimization: Detect and eliminate redundant, unnecessary test cases
- Ensure test requirements coverage: Extracting keywords from the Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- Predictive analytics: Forecast key parameters and specifics of end-users’ behaviors and identify application areas to focus on
- Defect analytics: Identify application area and defects that ties to business risks
What does this mean for organizations?
Even though there is a rising demand in prospects of AI/ML application in software testing, experts still regard AI/ML in testing is still in its infancy stage. However, we are very much likely able to see maturity coming.As AI is making new demands in testing and QA teams, Agile teams must start adopting AI-related skillsets—which include onboarding data science, statistics, mathematics. These new skillsets will not replace, but a complement to the core domain skills in automated testing and software development engineering testing (S-DET).
Also, business acumen is another essential skill to adopt. Successful testers need to have a combination of pure AI skills and non-traditional skills. Indeed, last year, new roles have been introduced such as AI QA analyst and test data scientist.
As for automation tool developers, they should focus on building tools that are practical. Companies are running PoCs and reassessing options to make the best use of AI and considering budgets. A good AI-assisted tool has to fulfill both the business cost-efficiency and the technical aspects such as reading production logs, generating test scenarios, or responding to production activities.
2. Test Automation in Agile teams
Test automation is undoubtedly no longer a foreign idea in quality assurance. Indeed, 44% of IT organizations expect to automate 50% or more of all testing in 2019. We predict that more adoption of automated testing will continue to be on the rise next year.As more businesses adopt the latest Agile and DevOps processes to fulfill the demand for Quality at Speed, test automation has become an indispensable component. Test automation continues to lead by helping teams perform repetitive tasks, detect bugs faster and more precisely, provide continuous feedback loops, ensure test coverage. Therefore, organizations that implement automated testing in their QA processes can save a significant amount of costs, time, and human resources.
Test automation in 2020 is expected to be championed especially by millennial entrepreneurs, leveraging the combination of open-source and commercial tools.
What does this mean for QA practitioners?
Test automation, however, will not eliminate manual testing. In fact, robust QA teams must appropriately combine manual and automated testing to achieve the most in ensuring software quality. The role of automated testing is undeniable—but some testing types such as exploratory or usability testing still need to be manually carried out.QA practitioners, in addition, have to develop a smart, common, and end-to-end environment. There has been an increasing need to automated from build through deployment. Test automation is no longer regarded as a functional but as a full-cycle requirement.
This process is easier said than done. That’s why many organizations have not been able to squeeze the most out of automated testing and received the desired return on investment. The Capgemini World Quality Report suggests that instead of looking at automation as a capability, QA teams should think of it as a broad, smart, and connected platform.
What does this mean for test automation solution providers?
Test automation tools developers must continuously update and upgrade tools to fulfill QA teams’ demands. Future test automation solutions must follow some basic criteria, for example:- Easy to adopt and use for end-users at any testing level
- Provide smart frameworks, meaning letting issues resolve themselves See Autohealing Smart XPath and Katalon Smart Wait
- Ensure full test coverage and quality bugs detection
- Cross-platform testing for web, API, mobile, and desktop automation
- Integrate with CI/CD tools and allow Continuous Testing
- Integrate with intelligent dashboards and analytics for quality insights See Katalon TestOps
3. Big Data Testing
Big data has served an essential role in a variety of business sectors including technology, healthcare, banking, retail, telecom, media, and so on. There has been more focus placed on using data to segment and optimize decision-making processes.Big data testing allows industries to deal with huge data volumes and diverse data types. It also helps make better decisions with precise data validations, as well as enhancing market strategizing. Big data testing is no longer a new phenomenon. However, it is expected to grow exponentially as many industries are shifting toward a data-oriented world.
The trend of testing big data has been widely adopted, mainly because of the robust processes that most of the enterprises are following make the most of their marketing strategies. Big data testing is not an uncommon practice and it is expected to become popular in the next year. Therefore, we forecast that the need for testing big data applications will see a new rise in 2020.
4. QAOps: Quality Assurance Sees Changes in DevOps Transformation
If you haven’t heard of the term ‘QAOps’ yet, now’s the time.You might have been familiar with ‘DevOps’—a set of software development practices that combines development (Dev) and information technology operations (Ops). The goal of DevOps is to shorten the systems development life cycle (SDLC), while teams can focus on building features, fixing bugs, and pushes frequent updates that are in alignment with business objectives. DevOps abridges the collaboration between developers and business operationalists.
In the same spirit, QAOps helps increase the direct communication flow between testing engineers and developers by integrating software testing into the CI/CD pipeline, rather than having the QA team operate in isolation. In short, QAOps is defined in two key principles:
- QA activities should be incorporated into the CI/CD pipeline
- QA engineers should work in alignment with developers and be involved throughout the CI/CD process.
QAOps can be applied not only in giant tech companies but also in medium and small teams. This practice can be flexibly scaled down or up to fit any business size. Because more teams are gearing toward DevOps, we will expect to see QAOps as a growing trend in 2020.
5. IoT Testing
The rise of testing Internet of Things (IoT) devices was already prominent in 2019. The number of IoT devices all around the world will reach 20.5 billion by 2020, according to Gartner.IoT testing means testing the IoT devices for security assurance, ease of use, trustworthiness, compatibility of device versions and protocols, versatility of programming items, monitoring connection delay, scalability, data integrity evaluation, device authenticity, so on and so forth. IoT testing engineers often face an overwhelming amount of work in this area, especially with monitoring communication protocols and operating systems and multiple combinations of different elements of an IoT system. Therefore, QA teams should expand their knowledge and enhance their skills in usability, security, and performance IoT testing.
Another challenge that IoT testers will face in the upcoming years lies in strategies. Although IoT devices and applications have been growing exponentially, 34% of respondents said their products have IoT functionality, but their team still does not have a proper testing strategy, according to the World Quality Report.
6. Demands for Cybersecurity and Risk Compliance
The digital revolution brings about increasing security threats. CIOs and CTOs from almost every enterprise across all sectors continue to acknowledge the importance of security testing of their software, applications, network, systems. Software developing teams even work with their partners to make their products more resilient to threats, taking the cybersecurity shield to the next level.Testing for security helps secure not only transactions (be it money or data), but also protection of their end-users. Because cyber threats can take place in any form, at any moment, security testing will continue to be a popular topic in the following year.